What is Lipoma?
A lipoma is a non-cancerous growth of fatty tissue that forms slowly under the skin. They are typically soft, movable, and feel somewhat rubbery to the touch.
Lipomas can occur anywhere on the body where there is fat, but they are most commonly found on the back, neck, shoulders, abdomen, and arms. They range in size from a small pea to several centimeters in diameter, and some people may have more than one.
If you are experiencing these symptoms, book an appointment today at our clinic in Nandhivaram-Guduvancheri, Chennai
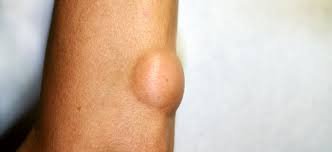
Symptoms
- Soft and movable
- Painless: Most lipomas do not cause pain unless they grow very large, press on nerves, or develop in an area that experiences frequent friction.
- Located just under the skin: They are usually superficial.
Causes
- The exact cause of lipomas is unknown, but they tend to run in families, suggesting a genetic component. They are more common in middle-aged and older adults. Injury to a specific area may also trigger their formation in some cases, though this is not always a direct cause.
What is a Sebaceous Cyst?
A sebaceous cyst (more accurately called an epidermoid cyst or pilar cyst, depending on their origin) is a closed sac under the skin filled with a cheesy or pasty substance called keratin. They form when a hair follicle or sebaceous gland (which produces oil for the skin and hair) becomes blocked, leading to a buildup of keratin and skin cells. They are most commonly found on the face, neck, scalp, and torso.
Sebaceous cysts often result from:
* Blocked ducts: A blocked sebaceous gland or hair follicle can trap keratin and oil, leading to cyst formation.
* Trauma: Skin injuries or surgical incisions can sometimes contribute to their development.
* Genetic conditions: In rare cases, some genetic syndromes can increase the likelihood of developing multiple cysts.
Symptoms of Sebaceous Cysts:
* Small, round lump: They are typically smooth to the touch.
* Movable under the skin: Similar to lipomas, they can often be moved slightly.
* Sometimes has a central dark spot: This is a tiny pore or “punctum.”
* May discharge a foul-smelling, cheesy material: This happens if the cyst ruptures or becomes infected.
* Can become tender, red, and swollen if infected.
When to See a Doctor for a Sebaceous Cyst:
Seek medical attention for a sebaceous cyst if:
* It becomes red, painful, or hot to the touch (signs of infection).
* It ruptures and drains pus or a foul-smelling substance.
* It’s growing rapidly.
* It’s in an area that causes discomfort or interferes with daily activities.
* You are concerned about its appearance.
General Information and Treatment Options for Both
Rubber Band Ligation:
Treat Internal hemorrhoids that protrude during bowel movements. Positioning a small rubber band over the base of the haemorrhoid, cut of its blood supply and causing to shrink and eventually fall of in a few days. The wound usually heals in one to two weeks. Mild discomfort and bleeding may occur. This treatment needs to be repeated for complete treatment of the hemorrhoids depending on the size or if they return.
Diagnosis:
Your doctor can usually diagnose a lipoma or sebaceous cyst based on a physical examination. In some cases, they may recommend further tests like an ultrasound, CT scan, or a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis, especially if there’s any suspicion of malignancy or if the lump has unusual characteristics.
Treatment Options:
Both lipomas and sebaceous cysts are generally benign and often do not require treatment unless they are causing symptoms, growing rapidly, or are a cosmetic concern.
* Observation: If the lump is small, painless, and not bothering you, your doctor may recommend simply monitoring it.
* Surgical Excision: This is the most common and effective treatment for both lipomas and sebaceous cysts. The procedure involves making a small incision to remove the entire lump. It’s usually performed under local anesthesia in an outpatient setting.
* Incision and Drainage (for infected cysts): If a sebaceous cyst becomes infected, your doctor may drain the pus to relieve symptoms. However, the cyst wall is often left behind, meaning the cyst can recur. Complete surgical removal of the cyst wall is usually recommended once the infection has subsided to prevent recurrence.
* Steroid Injections (for some cysts): In some cases, for inflamed but not infected cysts, a steroid injection may help reduce inflammation and shrink the cyst.
Important Note: Never try to pop or squeeze a lipoma or sebaceous cyst yourself. This can lead to infection, inflammation, and scarring, and may make subsequent medical treatment more difficult.
Living with Lumps and Bumps:
While discovering a lump under your skin can be concerning, remember that lipomas and sebaceous cysts are very common and almost always benign. The key is to be aware of your body and seek professional medical advice if you notice any new or changing swellings. Early evaluation can provide peace of mind and ensure appropriate management if needed.


 ACL Injury
ACL Injury Gall Bladder Stone
Gall Bladder Stone